INSULATION
SYSTEM
The Science of achieving Comfort within a Space
Thermal Insulation
Thermal insulation reduces the transfer of heat between objects with different temperatures. The most important aspect of an insulation material is its performance – that it consistently provides the designed-for resistance to the passage of heat throughout the lifetime of the building. Though the insulation manufacturer’s published performance expectations will be an essential guide, other factors associated with the ‘real-life’ installation of the material need to be considered as part of the design process:
Acoustic Insulation
Acoustic insulation absorbs, transmits, or redirects sound waves – vibrations in the air that pass through objects and result in audible sound. Noise, or unwanted sounds, is measured in decibels (dBA) and has a specific frequency distribution. In outdoor environments, reflective and damping materials are used in structures such as highway noise barriers.
Sound absorption of a material varies with the frequency of sound. Noise Reduction Coefficient is the mathematical average of absorption coefficient of a material at four frequency bands – 250, 500, 1000, 2000 Hz
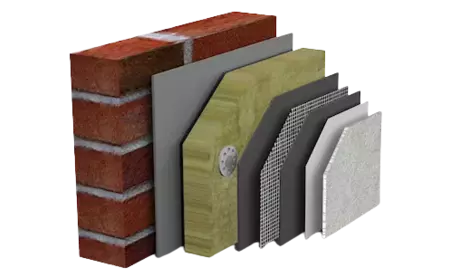
TYPES OF BUILDING INSULATION SYSTEMS

01.Glasswool Insulation
We are successfully ranked as the top importer & distributor of a broad assortment of Glass Wool. Our offered Glass wool is manufactured with precision using best grade raw material by our vendor’s experts. These Glass wools are used for thermal & acoustic insulation over false ceilings in various industries. The rock wools are inspected on several parameters for supplying a flawless range to customers.
Features:
Withstand in bad weather condition
Best for thermal insulation
Enhanced durability
02.Rockwool Insulation
Extensively used as a part in plant and building construction, our Rockwool Insulation is effective in saving energy and, consequently, money. Due to its feature of energy conservation, it contributes greatly in environment protection. We offer this product to clients based across the country at the most affordable prices.
Features:
The micro structure fibres present in rockwool slabs enables it to absorb the sound and decrease the noise developed by reflection. Additional benefit of best Fire Retardant property.


